Regular mode
This is the regular mode of the device. In this mode, the controller processes the recorded program and the Mervis HMI website and other Mervis services communicating with the controller are also available. The device enters this mode a few seconds after plugging in the power supply. The mode is physically indicated by PWR LED continuous emitting and RUN LED emitting with short flashes (demonstration here / startup simulator here).
First connection of the controller
Unipi Patron controller size S must be powered by 24 V⎓ power supply; 0.63 A, sizes M and L must be powered by 24 V⎓ power supply; 1,5 A. To access the introductory HMI web page, it is necessary to connect to the controller from a computer or tablet, with any modern web browser.
For the programming option, it is necessary to connect to the controller from a computer with the MS Windows 10 operating system or higher with the Mervis IDE installed. The installation procedure is described below.
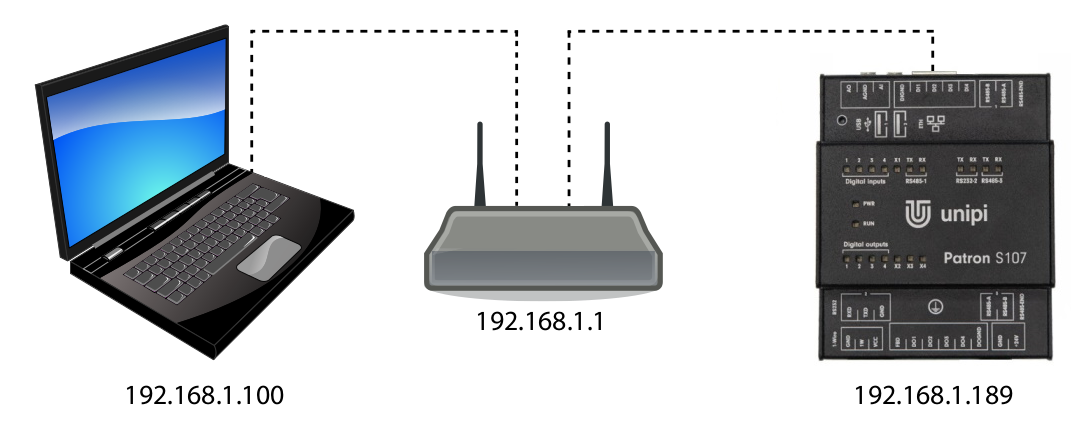
Connection via local network with DHCP server
Despite its somewhat complex name, this approach is a simple and most commonly used variant. All you have to do is connect the controller to a computer network using an Ethernet cable and connect a computer or tablet (either via an Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi) to the same network. Your DHCP server (router or Wi-Fi router) on this network will automatically assign an IP address to both of them from the available range.
The IP address of the controller can be found either from a DHCP server or by a suitable program to scan the network (such as Advanced IP Scanner). In most cases, however, an mDNS address variant will suffice.
The IP addresses used are only examples.
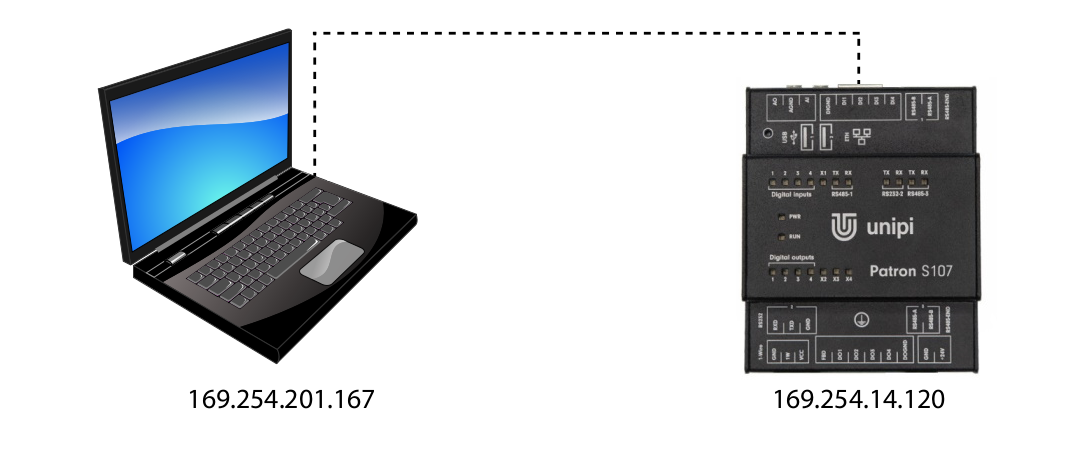
Direct connection
A direct connection requires the physical connection of the computer and controller with an Ethernet cable. Because this solution does not include a DHCP server, both the computer and the controller automatically assign itself a random IP address from the range 169.254.XXX.XXX.
You can find the IP address of the controller with a suitable program for scanning the network (such as Advanced IP Scanner). In most cases, however, an mDNS address variant will suffice.
The IP addresses used are only examples.